Search
Democracy Links
Member's Off-site Blogs
the big bowser .....
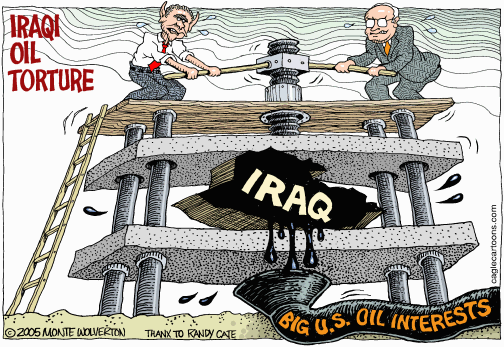
When President George W. Bush launched the invasion of Iraq in March 2003, his overarching goals all revolved around the geopolitics of oil. He and his top officials were intent on replacing Saddam Hussein's regime with one that would prove friendly to American oil interests. They also imagined that, greeted as liberators by a grateful population, they would preside over a radical upgrading of Iraq's petroleum capacity, thereby ensuring adequate supplies for American consumers at an affordable price. Finally, by building and manning a constellation of major military bases in a grateful Iraq, they saw themselves ensuring continued American dominance over the oil-soaked Persian Gulf region, and so the energy heartland of the planet.
All of this, of course, proved to be a mirage. The U.S. invasion and ensuing occupation policies provoked a bitter Sunni insurgency that quickly overshadowed all other American concerns, including oil. As a result, no matter how much money they poured into the task, the Bush administration and its Baghdad agents found themselves incapable of boosting petroleum output even to the levels of the worst days of Saddam Hussein's regime - and so their plans to use oil revenues to pay for the war, the occupation, and the reconstruction of the country all vanished into thin air.
The data provided by BP on yearly production tallies cannot be starker when it comes to the impact on oil output of the insurgency, rampant corruption, the loss of the nation's oil professionals (many of whom fled into exile amid sectarian warfare), and other related factors. Prior to the American invasion, Iraq was pumping 2.6 million barrels of oil per day, already significantly below its pre-invasion peak of 3.5 million barrels per day. In the first year of the ill-starred U.S. occupation, production quickly plunged to a paltry 1.3 million barrels per day. Only in 2007 did it finally top the two million mark and, with improved security, 2.4 million in 2008. Assuming conditions continue to improve, Iraqi output could, for the first time, exceed pre-invasion levels, though barely, in 2009 or 2010 - six years or more after Baghdad fell to American forces.
- By John Richardson at 16 Jul 2009 - 10:01pm
- John Richardson's blog
- Login or register to post comments
Recent comments
2 hours 30 min ago
3 hours 53 min ago
4 hours 48 sec ago
14 hours 5 min ago
14 hours 49 min ago
15 hours 9 min ago
15 hours 16 min ago
15 hours 27 min ago
17 hours 34 min ago
18 hours 13 min ago